The Ion AmpliSeq Designer links the output designed bed file directly to the UCSC Genome Browser automatically configured with the dbSNP and Repeat Masker annotation tracks. While this allows the user to determine if the regions were filtered based on either repeat regions or SNPs under the 3’ primer, the designer also filters for other reasons. This portion of the User Guide is meant to offer the user some suggestions for using other bioinformatics tools to determine the quality of the design and for diagnostic and research purposes.
Minimizing Off-Target Hybridization
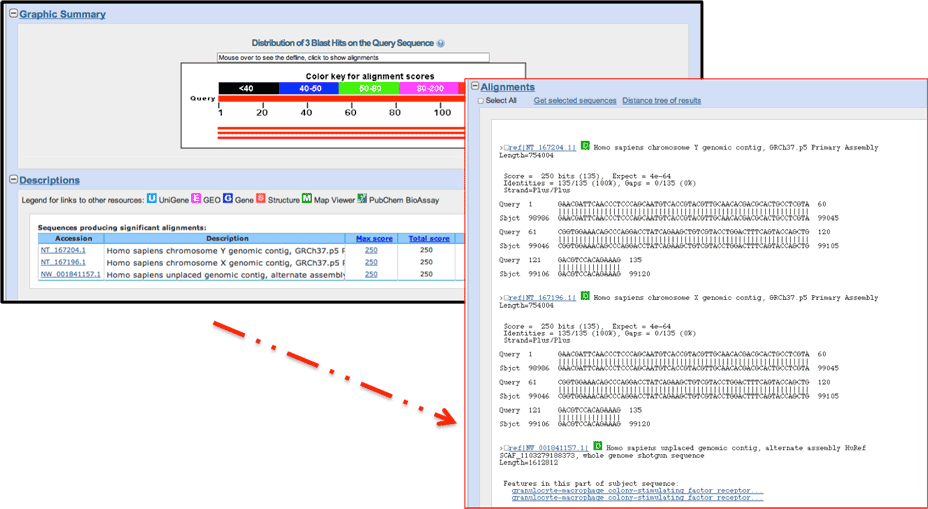
One common reason the designer may have filtered the region would be that it is a non-unique sequence and would hybridize in other areas of the genome and thus be deleterious to your reaction. BLAST, the Basic Local Alignment Search Tool, finds regions of local similarity between sequences.
Using the UCSC Genome Browser, you can enter the region that has been filtered in the results of your design.
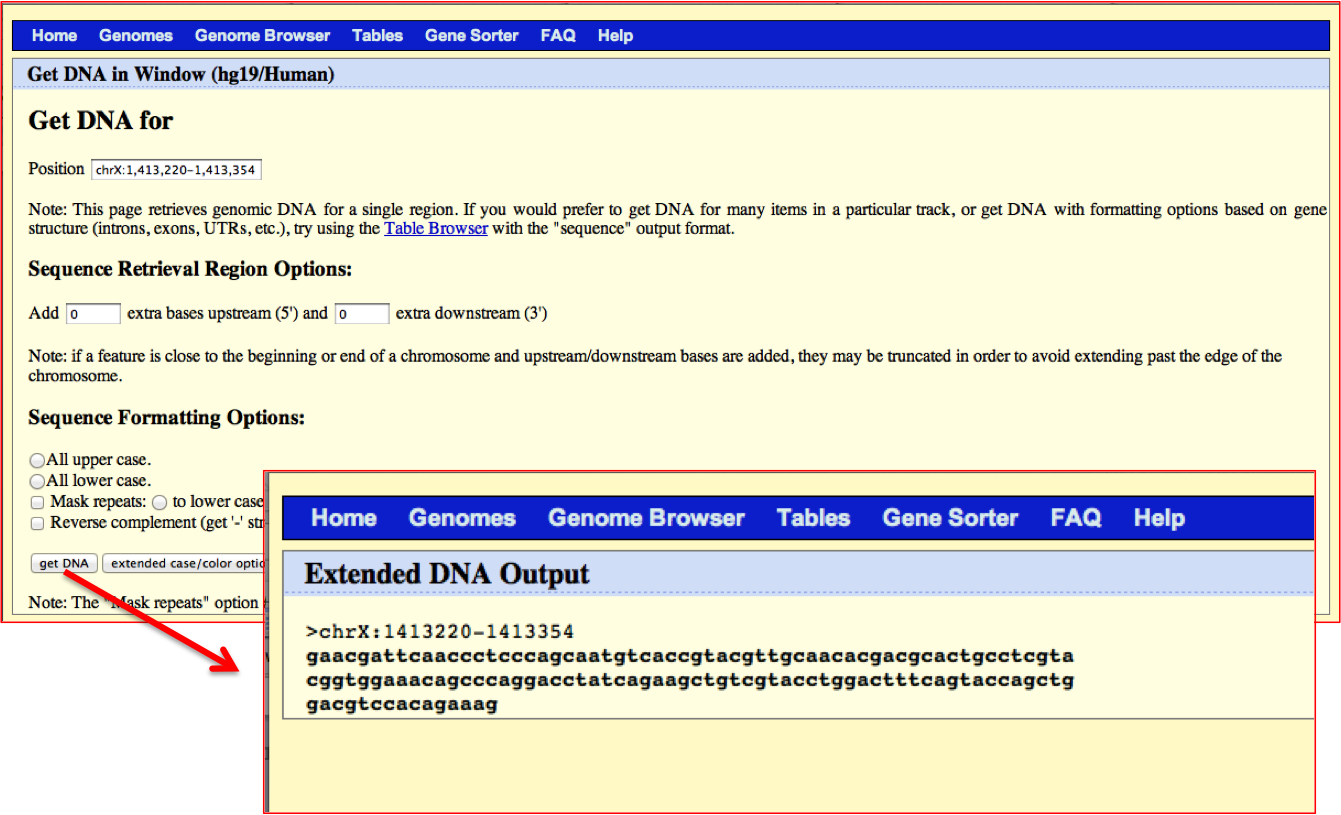
Copy the sequence, and run a BLAST search on this sequence.
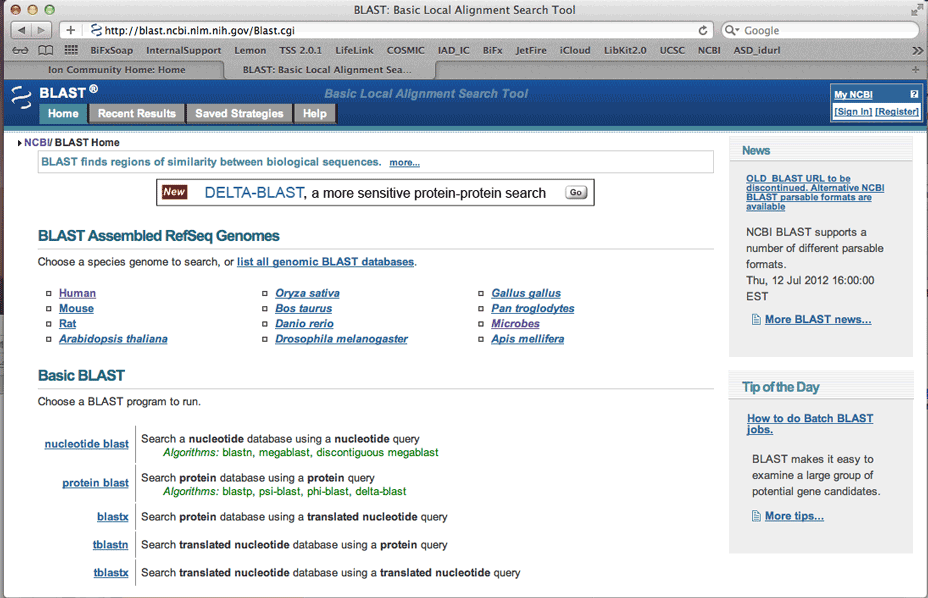
Be sure to select Human, running a nucleotide query.
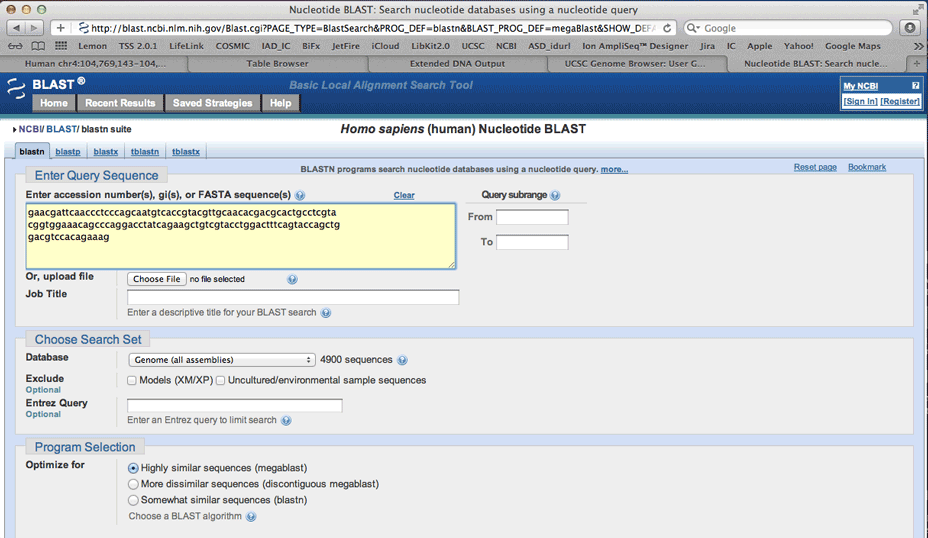
If the search returns multiple results for that query, the designer has filtered this to minimize off-target hybridization.
Determining GC-content
The designer filters regions that have either very high or very low GC % content. Using the UCSC Table Browser, select the Mapping and Sequencing Tracks and GCcontent track options.
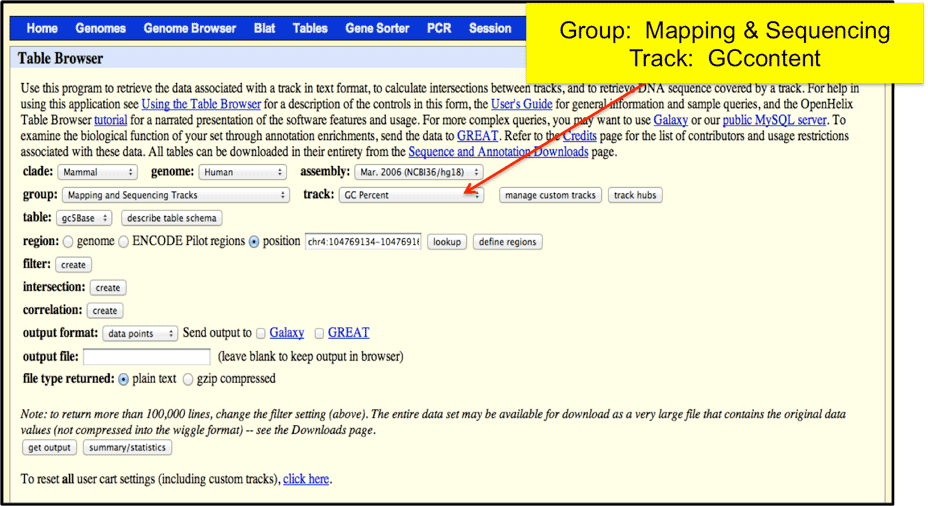
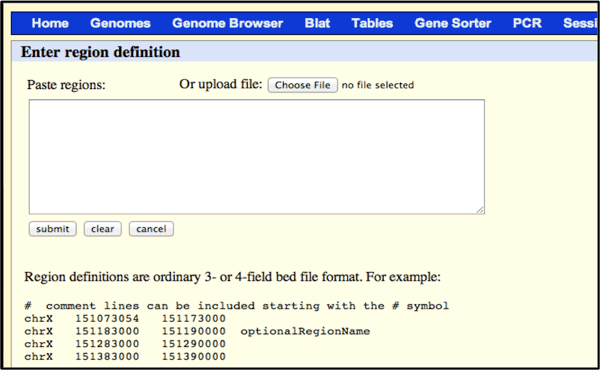
You can enter to search for a specific region, or chose to upload your designed bed file to the Browser. The output will be in a 5-basepair sliding windows where you can determine regions that are below 20% or above 80% in GC content.
Torrent Browser Plugins
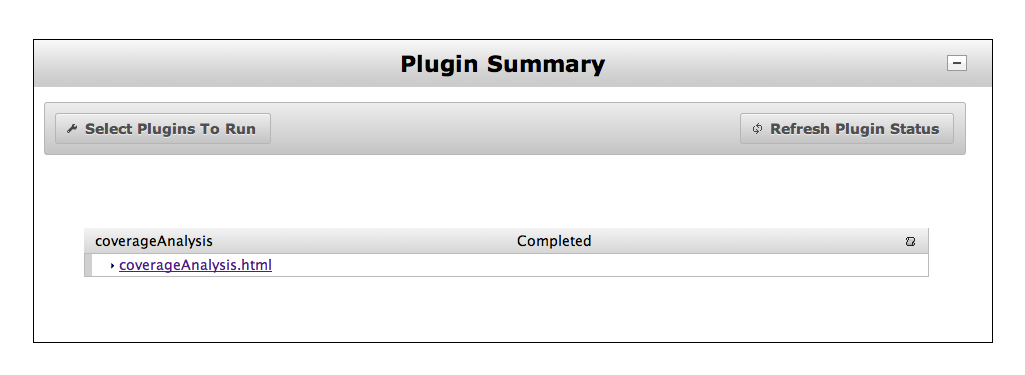
You can use the coverageAnalysis Plug-in on your Torrent Browser to determine coverage uniformity of your sequence run. Details on using the coverageAnalysis Plug-in can be found in the Torrent Suite™ Software 5.12 User Guide.